Ethereum: Key derivation in HD wallets using the extended private key vs hardened derivation
Key performance in HD wallets: Choosing between extended private key and hardening performance
When it comes to managing Ethereum wallets, choosing the right key derivation function (KDF) is crucial to securing your private keys. In this article, we will explore two popular options of KDF used in HD wallets: an extended derivative of a private key and a hard -to -hard performance of a private key.
Extended private key performance
The extended derivative of the private key uses the more complex algorithm to generate a child’s private key from the parent public key. Users often prefer this method because of their larger safety features, but can also lead to longer key sizes. In Chapter 4 “Mastering Bitcoin”, the book mentions that an extended derivative of a private key usually requires at least 256 bits per private key.
Solid Private Key Performance
The hardening performance of the private key uses a simpler algorithm with fewer parameters than the prolonged private key performance, making it faster and more appropriate for use. However, this method can endanger some security features, such as the possibility of protection from certain types of attacks or recovery of lost keys.
HD wallets and choosing kdf
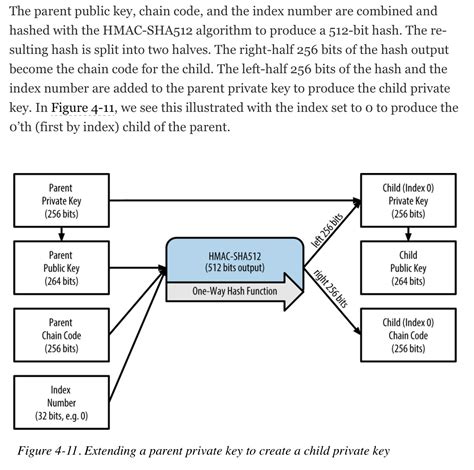
In HD wallets, you usually have two main options for key performance:
- Extended private key performance : This is often used in full HD wallets, which provide a safer and more private way to store Ethereum keys.
- Solid Private Key performance : This method can be used in a part of HD wallets or hybrid wallets that combine both prolonged and harden KDF.
Choosing the right KDF for your wallet
When you choose KDF for your wallet, consider the following factors:
* Security level : If priority priority with high security features, use an algorithm of prolonged private key. For lower safety requirements, the hardening can be sufficient.
* Key size : Extended private key derivative usually requires longer keys (at least 256 bits per private key), while hardening can generate shorter keys (usually up to 24 bytes).
* Practical VS Safety : If the speed is crucial, use faster kdf like solidity. If security is your main priority, stick to the extended algorithm.
Conclusion
Choosing the right function of keys in HD wallets can be confused by compromise between safety and convenience. Understanding the differences between prolonged private key performance and a solid dedication of a private key, you will make informed decisions on which method is best for your wallet and needs. Remember to consider your priorities when selecting KDF for a safe and appropriate management of the key to Ethereum.
additional resources
- “Mastering Bitcoin” Andreas M. Antonopoulos
- Ethereum documentation: [www.ethereum.org] (
- HD Wallet guides: [e.g. Ledger Live, Treasury Wallet]